The Imprivata Site
Download a PDF for a complete guide to organize your Imprivata appliances and the computers they serve to optimize redundancy, successful failover, and uninterrupted service to users.
Imprivata Sites for G3 Enterprises
In a G3 (third generation) Imprivata enterprise, appliances and the computers they serve are grouped into Imprivata sites for administration of security, compliance reporting, and service availability.
Availability requirements have a significant impact on the number of appliances to configure in each G3 site. Within each site, consider configuring additional appliances than required to serve endpoint computers in that site, to accommodate for an appliance failure with zero interruption or degradation of service. User sessions are replicated among the appliances within a site; if an appliance fails the Imprivata agents migrate seamlessly to another appliance in the site. This behavior is configurable from the Imprivata Admin Console. Users are not required to log in again.
Appliances in multiple sites can provide fault tolerance by serving as backup to one another. The Imprivata database, including user enrollments, policies, and single sign-on services, is constantly synchronized among all Imprivata appliances at all sites in a G3 enterprise. If all appliances in a site are inaccessible, Imprivata agents can communicate with appliances in other sites (as configured by the administrator) and the switchover occurs automatically, although users may need to reauthenticate to Imprivata. When planning for failover capacity, remember to allocate enough appliances in each failover site to provide acceptable levels of service for both original and failed-over users.
An Imprivata enterprise can include any number of Imprivata sites. Imprivata G3 sites normally map to LANs within the enterprise. The following illustration shows a sample Imprivata G3 enterprise.
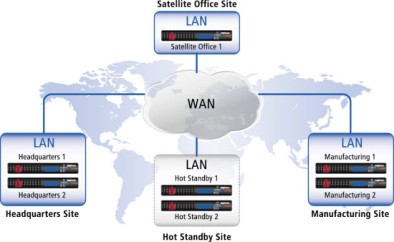
Appliances in a G3 site typically serve endpoint computers located in a geographical area served by a data center.
The Sites page in the Imprivata Admin Console (gear icon > Sites option) lists the sites and some information about the appliances in the sites. To review the details of a site, click on the site name on the Sites page to open the Imprivata site record. The contents of an Imprivata site record are detailed in
NOTE: To rename a site, go to the Imprivata Appliance Console Enterprise page, click the site you want to rename, change the name, and click OK. The change takes a few minutes to propagate throughout the enterprise.
Imprivata Sites for G4 Enterprises
Imprivata appliances and the endpoint computers they serve are grouped into Imprivata sites differently in a G4 (fourth-generation) Imprivata enterprise than in a G3 (third-generation) enterprise. In a G4 enterprise, only one or two sites are used, and Imprivata recommends a maximum of two sites. Although a G4 enterprise can include any number of sites, having more than two sites no longer serves any purpose. Imprivata G4 sites can cover WANs spanning geographic continents. For appliances in the one or two sites in a G4 enterprise, you can choose large enough disk and RAM sizes, and add service appliances to a data center if needed, to provide efficient authorization service to all users in a large organization. For more information on G4 appliance sizing and numbers, see
Also, appliances in a G4 enterprise can fail over to each other without requiring additional sites. This is described below in Imprivata Agent Failover and Fault Tolerance.
A G4 enterprise typically contains one database appliance in each of two geographically distant data centers, and zero to four service appliances total in those same or nearby data centers, depending on capacity needs. Imprivata strongly recommends that the two database appliances in a G4 enterprise be deployed to different data centers, preferably in different geographic regions or locations. That way if one data center loses power or becomes unreachable, the other data center can service all endpoints in the enterprise.
Typical G4 enterprise site configurations are:
-
A single site with an "active/active" setup: All appliances service endpoint agent authorization requests. The site has the recommended two database appliances for redundancy. This single-site setup works whether or not data centers are geographically dispersed. However, having dispersed data centers and having the two database appliances in different geographic regions provides greater resilience.
-
Two sites with an "active/active" setup: All appliances in each site service endpoint agent authorization requests for that site. The enterprise has the recommended two database appliances, one in each site, for redundancy. Each site is assigned as the failover for the other site.
G4 enterprises avoid the resources and cost of a hot standby site: In a G4 enterprise, an active/active setup with enough appliances of sufficient capacity can handle data center failover and provide efficient authorization service to all enterprise users, without needing the extra resources and cost of a hot standby site. In a sample hot standby "active/passive" setup, pairs of one database appliance and one service appliance are deployed in each of two sites. At one site, both appliances service all endpoints, and the other site acts as a hot standby site for disaster recovery. Imprivata supports this active/passive setup, but it is not optimal for G4 enterprises. The hot standby site appliances are not used to service authorization requests, which places a greater service burden on actively used appliances. In particular, the second database appliance in a G4 enterprise has resource capacity that is too valuable to sit effectively idle.
In an enterprise with two database appliances, if one database fails or becomes unreachable, agents automatically redirect to the remaining database. If a database appliance goes down or becomes unreachable for the indefinite future, for example due to a natural disaster, immediately add a replacement database appliance to the surviving site or data center.
Availability requirements have a significant impact on the number and capacity of appliances to configure in a G4 site and enterprise. Consider configuring more appliances or larger capacity appliances than are required to serve endpoint computers in a site and enterprise, to accommodate for an appliance failure with zero interruption or degradation of service.
User sessions are replicated among the database appliances in a G4 enterprise, regardless of their site. If an appliance fails, the Imprivata agents redirect seamlessly to another appliance in the site. This behavior is configurable from the Imprivata Admin Console. Users are not required to log in again after the redirection.
Appliances in two sites can provide fault tolerance by serving as backup to one another. The Imprivata database, including user enrollments, policies, and single sign-on services, is constantly synchronized between the two database appliances, independent of site, in a G4 enterprise. If all appliances in a site become inaccessible, Imprivata agents can communicate with appliances in the other site (as configured by the administrator) and the failover occurs automatically, although users may need to reauthenticate to Imprivata. When planning for failover capacity, allocate enough appliances with sufficient capacity in each failover site/location to provide acceptable levels of service for both original and failed-over users.
The Sites page in the Imprivata Admin Console (gear icon > Sites option) lists the sites and some information about the appliances in the sites. To review the details of a site, click on the site name on the Sites page to open the Imprivata site record. The contents of an Imprivata site record are detailed in
NOTE: To rename a site, go to the Imprivata Appliance ConsoleEnterprise page, click the site you want to rename, change the name, and click OK. The change takes a few minutes to propagate throughout the enterprise.
There are two types of Imprivata sites:
- Active sites — Handle daily Imprivata service for all agents on computers within their IP range.
- Hot standby sites — Stand idle until an active site fails over to the hot standby. A hot standby site is always current with the latest Imprivata data.
Active sites can fail over to each other. An Imprivata enterprise is not required to include any hot standby sites. G4 enterprises do not need hot standby sites, which are not optimal for G4 enterprises, as described in the previous section.
How Imprivata Agents Determine the Home Site
Each agent determines its home site based on the host computer's IP configuration. Each active site has a list of IP address ranges for subnets belonging to this site. The list of IP address ranges must be set up by the Imprivata administrator.
Imprivata matches the agent host's IP address against any range in any site. If a range is found then the site owning this range is considered to be the home site for the agent.
If this direct IP matching fails, the agent analyzes the routing table on the computer. The route lookup attempts to identify a route that covers any IP range for any site. Route lookup helps to determine the location for a VPN client outside the corporate network when direct IP address matching does not work.
IP ranges help determine the preferred site to use, rather than restrict access. If there is a non-default route to the host network, Imprivata route rules will choose the first of several sites with restrictive IP ranges within the corporate network sub-net.
Imprivata connects to external servers such as domain controllers and ID token servers. You can assign specific external servers to any Imprivata site, overriding the enterprise setting.
If you want to point different Imprivata appliances to unique external servers, you must define separate sites. For example, if you have one domain controller in London and one in New York, you could create two Imprivata sites and point each one to the relevant domain controller.
Connecting to a Domain
Each site can communicate with any external server reachable on the network, but sites usually connect to local directory servers (domain controllers).
User account information from each directory is replicated across all appliances in the site and across the enterprise, so there is no need to connect to user directories that are local to other Imprivata sites.
To view a list of domains and connections, go to the Users menu > Directories page in the Imprivata Admin Console:
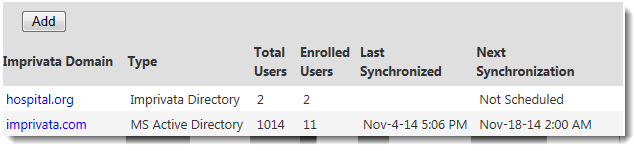
From the Directories page, you can specify the host name of a user directory server for each domain.
Connecting to an External Token Server
Imprivata supports ID token authentication with VASCO OTP tokens and RSA SecurID tokens.
- VASCO OTP tokens are best managed through the Integrated VASCO OTP Tokens Authentication option, which provides an internal VASCO VACMAN server built into Imprivata.
- RSA SecurID tokens and Secure Computing SafeWord tokens require a connection to an external ID token server.
ID token server connections are available to all Imprivata sites.
You can deploy only one type of external ID token server in an enterprise, but this limit does not affect the Integrated VASCO OTP Tokens Authentication option. This makes it easy to migrate from one ID token type to another.
Imprivata agents have a built-in mechanism for selecting an appliance. This section describes the rules by which an agent selects an appliance.
Agent starts for the first time —The agent retrieves the Imprivata enterprise topology: the full configuration of appliance and sites. The appliance specified by the IPTXPrimServer registry setting is used as the bootstrapping appliance for this purpose. After the topology is downloaded, rules in the topology are used to find the server to be used in communication. If the enterprise topology changes, the new topology is pushed to all Imprivata agents in the next update from the appliance. The new topology will then be evaluated when a new session is started, or on failover.
Subsequent agent connections — The agent first attempts to connect to a random appliance in its home site. It continues to use this appliance for new user sessions for a period of three hours. After three hours, the agent will attempt to connect to a different random server within its home site, for load balancing. If no other server is available, it will use the same server. This only applies to new sessions. It does not affect active running sessions — they will remain served by the same appliance. Active sessions are also not affected by any changes in the enterprise topology, as long as their appliance is still available.
If an agent cannot communicate with any appliance in its home site, it will try to fail over to a random appliance in another site — first the primary, then the secondary failover sites as specified by the Administrator. (Secondary failover sites typically are not used in a G4 enterprise, for which Imprivata recommends having at most two sites.) If an agent cannot find any appliance to connect to, it will attempt to connect to the IPTXPrimServer appliance — the "last resort" appliance. This allows recovery from situations when the topology is mis-configured and the agent cannot connect to any server.
An agent that cannot communicate with an appliance goes into offline mode. Further attempts to communicate with servers are done in the background, according to the interval set by the Administrator.
Agents come back online when they successfully connect through the process described above — on each authentication attempt the agent tries all of these strategies. This accommodates for changes in routing table configurations.
For fault tolerance within a site that has multiple appliances, Imprivata can accommodate a failure of an appliance with no interruption or degradation of service. Deploying additional appliances at a site can provide higher levels of availability. Failover within a site is described in Agent Connection/Failover within a Site.
Appliances in multiple sites in a G3 enterprise, or in typically at most two sites in a G4 enterprise, can provide fault tolerance by serving as backups to one another across sites over a WAN. User enrollments, policies, and SSO data are constantly synchronized among sites in a G3 enterprise, or among database appliances (independent of sites) in a G4 enterprise.
If all appliances in a site are inaccessible, Imprivata agents can communicate with appliances in other sites and the switchover occurs automatically. If an entire site is down, agents can be served by appliances at another site. Failover between sites is detailed in Agent Failover Between Sites.
On the Imprivata Admin Console, go to the gear icon menu > Sites page to view your site topology. Imprivata sites service computers with IP addresses within a range set in the site record accessible on the Sites page. For details see